Artificial Intelligence in Health Care: Top Innovations and Their Impact on Patient Care
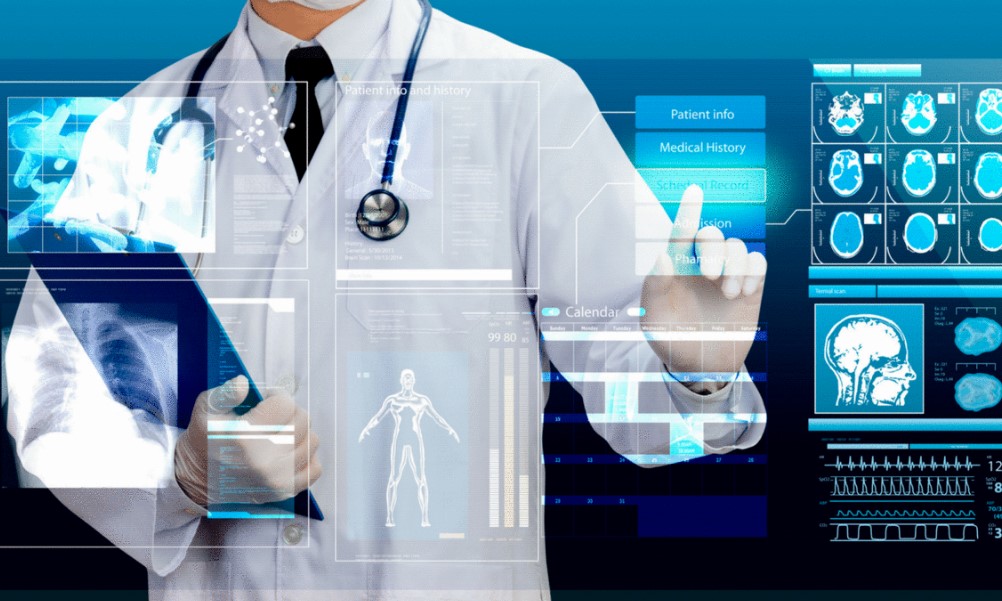
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping health care with powerful, data-driven tools that assist professionals in diagnosing diseases, personalizing patient care, and optimizing administrative workflows. AI in health care represents the integration of sophisticated machine learning, natural language processing, and other AI technologies with existing medical practices to produce precise, efficient, and personalized health services. This article explores how Artificial Intelligence in Health Care functions, the real-world benefits it provides, and the innovative products driving these changes. By the end of this guide, you’ll understand how AI is transforming health care and get insights into choosing the best AI-powered tools for specific needs.
What Is Artificial Intelligence in Health Care?

Artificial Intelligence in health care refers to the deployment of advanced algorithms and data processing techniques to improve various aspects of medical practice.
By analyzing large volumes of medical data—such as patient records, imaging results, and genetic information—AI systems are able to detect patterns, assist in decision-making, and even make accurate predictions regarding patient health outcomes.
These systems leverage powerful machine learning models that “learn” from historical data to make informed decisions that aid health professionals.
Types of Artificial Intelligence in Health Care

Artificial Intelligence (AI) in health care has developed into several types, each serving unique roles in enhancing patient outcomes, streamlining medical processes, and improving diagnostic accuracy. Here are some of the key types of AI applied in health care today.
1. Machine Learning (ML)
Machine Learning (ML) is one of the most widely used AI types in health care. ML algorithms analyze large datasets to identify patterns that can support clinical decision-making. In health care, ML aids in predicting disease outcomes, identifying at-risk patients, and detecting health issues earlier than traditional methods. For instance, ML algorithms applied to medical imaging can help detect abnormalities like tumors or fractures more accurately, assisting radiologists in making faster diagnoses.
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables computers to understand and interpret human language. In health care, NLP can process unstructured data from clinical documentation, extracting valuable information that doctors can use to make better-informed decisions. This includes summarizing patient records, scanning medical literature for relevant research, and supporting electronic health records (EHR) management. By reducing the time physicians spend on administrative tasks, NLP allows them to dedicate more time to patient care.
3. Robotics
Robotics in health care utilizes AI to perform tasks that are traditionally human-operated but are now assisted by intelligent systems. Robotic surgery, for instance, allows for minimally invasive procedures where the robot acts with high precision under a surgeon’s control. Additionally, robots are also used in rehabilitation, assisting patients with physical therapy, and in elderly care, where they provide assistance and monitor health conditions.
4. Rule-Based Expert Systems
Expert systems are AI programs that mimic the decision-making abilities of human experts. These systems use predefined rules and knowledge bases to analyze complex information, making them helpful for diagnosing diseases and recommending treatment plans. They’ve been particularly useful in areas like oncology and cardiology, where precision is crucial. Although they lack the flexibility of ML systems, expert systems still play a valuable role in providing reliable, consistent medical advice.
5. Image and Signal Processing AI
This type of AI focuses on analyzing images (e.g., X-rays, MRIs) and biological signals (e.g., heart rate, brain waves). Image and signal processing AI is pivotal in diagnostics, helping to identify abnormalities in medical scans and monitoring patients’ vital signs in real time. In cardiology, for example, AI systems can analyze ECG patterns to detect potential cardiac issues earlier, giving doctors a critical advantage in treatment.
Key Functions of Artificial Intelligence in Health Care

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping the health care sector by enhancing diagnostics, treatment personalization, predictive analytics, and operational efficiency. Here are the core functions of AI in health care, demonstrating how it addresses critical needs and optimizes health outcomes.
1. Enhanced Diagnostics
One of AI’s primary roles in health care is improving diagnostic accuracy and speed. AI-driven tools, especially those using machine learning and deep learning algorithms, analyze medical images, lab results, and patient records to detect diseases early. For instance, in radiology, AI systems can analyze X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans to identify patterns associated with conditions like tumors, fractures, or organ abnormalities, often faster than human analysis. This rapid diagnosis allows for early intervention, which is crucial for better patient outcomes and can reduce the need for invasive tests.
2. Personalized Treatment Plans
AI plays a critical role in customizing treatments to individual patients by analyzing genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Known as precision medicine, this approach enables health care providers to tailor treatments based on each patient’s unique characteristics. For example, in oncology, AI analyzes genetic data to identify specific mutations in cancer cells, guiding doctors in selecting treatments that target those mutations. This personalization can make therapies more effective and reduce adverse effects, as treatment is better aligned with the patient’s profile.
3. Predictive Analytics
AI is increasingly used for predictive analytics in health care. By analyzing large sets of patient data, AI algorithms can predict disease outbreaks, patient readmission risks, and potential complications. For example, hospitals use AI to assess patient risk factors and predict readmission likelihood, allowing medical staff to implement preventive measures and improve patient management. In public health, predictive AI models help forecast disease outbreaks by analyzing factors like population movement and environmental conditions, aiding in preparedness and resource allocation.
4. Operational Efficiency and Workflow Optimization
Beyond patient care, AI is transforming the operational aspects of health care. AI-powered tools streamline administrative tasks, manage patient flow, and optimize resource allocation. In hospitals, AI can automate scheduling, monitor bed availability, and even manage inventory for critical supplies. By reducing the administrative burden on health care workers, AI allows them to focus more on patient care, enhancing overall productivity and reducing operational costs.
5. Virtual Health Assistance and Patient Monitoring
AI-enabled virtual assistants provide real-time support to both patients and medical staff. These virtual health assistants answer patient queries, send medication reminders, and monitor vital signs through wearable devices. This real-time monitoring allows for early intervention when abnormal readings are detected, improving patient safety, especially for those managing chronic conditions.
These key functions of Artificial Intelligence in health care reflect its potential to improve both the quality of care and the efficiency of health care systems, making it a transformative technology for the medical field.
How Artificial Intelligence in Health Care Works
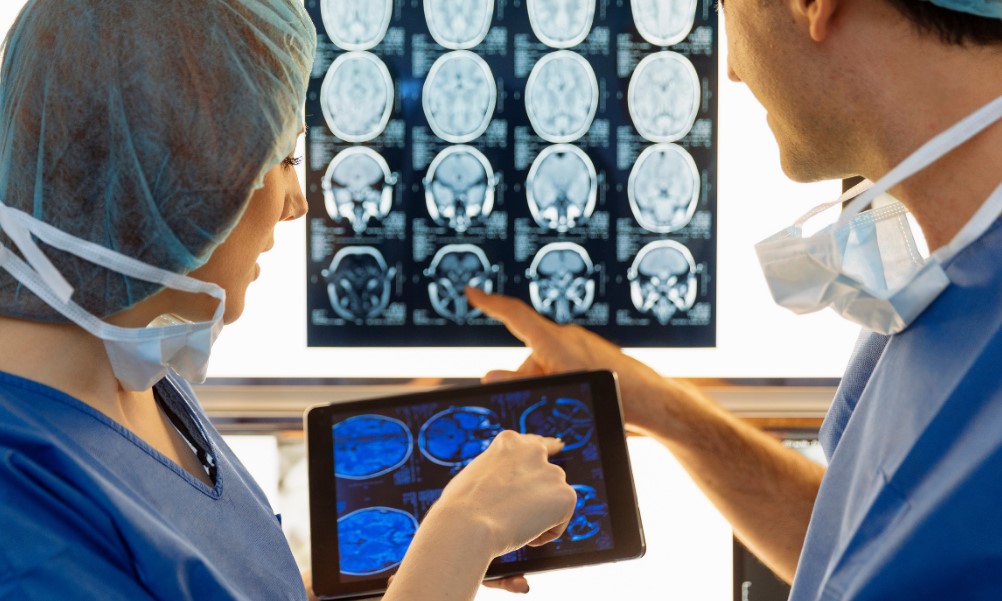
Machine Learning in Medical Diagnosis
Machine learning, a core component of AI, allows systems to “learn” from large datasets, making it possible to detect patterns within medical data that might go unnoticed by human eyes. The Machine learning models trained on extensive sets of medical images, for example, can identify certain types of cancer cells or fractures, assisting radiologists in the diagnosis process.
The learning process typically involves supervised learning, where a machine learning model is trained on labeled datasets, such as confirmed medical diagnoses. Over time, the model’s accuracy improves, resulting in reliable diagnostic tools that can enhance or even outperform human evaluations in specific contexts.
Natural Language Processing for Clinical Documentation
Natural Language Processing (NLP) in AI allows health care systems to interpret and analyze free-text information within clinical documentation. This feature is highly beneficial as it enables AI systems to “read” patient records, research papers, and ongoing clinical studies to pull out relevant information quickly. Health care professionals use NLP-powered tools to gain insights from massive volumes of data, which may otherwise be time-consuming to analyze manually.
Benefits of Using Artificial Intelligence in Health Care
Improved Diagnostic Accuracy and Speed
AI in health care significantly enhances diagnostic accuracy. Machine learning algorithms can process data from millions of medical cases, identifying disease markers with precision. For example, AI can detect early-stage tumors in medical images, enabling treatment to begin sooner, which is critical for patient survival rates.
The speed of AI-powered diagnostics is also a major advantage, especially in emergencies. AI can process imaging data within seconds, providing critical information to doctors, who can then make fast, informed decisions.
Enhanced Treatment Personalization
AI enables more precise, patient-centered care by personalizing treatment plans based on a patient’s health data. In oncology, for example, AI analyzes genetic information to tailor chemotherapy treatments to individual patients, reducing side effects and improving treatment efficacy. Personalized care fosters better health outcomes by addressing unique patient needs.
Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings
AI optimizes administrative tasks, managing patient records, appointment scheduling, and medical billing more efficiently. Health facilities that incorporate AI tools into their workflows can significantly reduce operational costs and free up resources to focus on direct patient care.
Top AI Solutions in Health Care
Several products stand out as prime examples of Artificial Intelligence in Health Care, addressing specific needs within the medical field. Each product offers unique features and use cases, as outlined below.
IBM Watson Health
IBM Watson Health is a pioneering AI system that combines data analytics with machine learning to support medical decision-making. Watson Health uses data-driven insights to help oncologists, radiologists, and other specialists make informed treatment decisions.
- Use Case: IBM Watson Health is frequently used in oncology to analyze genetic profiles, assisting oncologists in developing targeted cancer treatment plans.
- Pros: Accurate diagnostics, extensive data integration, reliable support for medical professionals.
- Cons: High cost, requires specialized training to integrate.
- Price: IBM Watson Health’s pricing varies based on the chosen solutions. Custom pricing is available upon consultation.
- Where to Buy: For more details, visit IBM Watson Health’s official website.
PathAI
PathAI is a leading platform that uses deep learning to assist pathologists in diagnosing diseases. This AI tool is especially beneficial in detecting cancer cells in biopsy samples, allowing for quick and accurate diagnoses.
- Use Case: PathAI enhances pathologists’ diagnostic accuracy in cancer cases by providing detailed image analysis.
- Pros: Accelerates diagnosis time, improves diagnostic accuracy.
- Cons: Primarily available in larger medical centers.
- Price: Subscription-based; direct consultation is recommended for specific pricing.
- Where to Buy: PathAI’s tools are available via PathAI’s official website.
Tempus
Tempus focuses on precision medicine by analyzing clinical and molecular data to help in creating personalized treatments, particularly in oncology. The Tempus integrates data from clinical tests, genetic profiles, and molecular imaging.
- Use Case: Tempus is instrumental in oncology, where it helps oncologists develop customized treatments based on genetic information.
- Pros: Highly effective for personalized cancer treatment, integrates complex data sources.
- Cons: Expensive and limited availability in smaller clinics.
- Price: Tempus pricing requires a consultation to discuss options based on specific patient needs.
- Where to Buy: More details are available on Tempus’s website.
Aidoc
Aidoc uses advanced AI algorithms to analyze medical images and quickly identify abnormalities. It is widely used in emergency rooms to detect critical conditions such as brain bleeds and fractures.
- Use Case: Aidoc is particularly valuable in emergency settings, providing fast, accurate imaging analysis for critical cases.
- Pros: Speeds up emergency diagnoses, easy integration with imaging systems.
- Cons: Initial setup cost can be high.
- Price: Aidoc’s pricing is available upon consultation.
- Where to Buy: For more information, visit Aidoc’s website.
Zebra Medical Vision
Zebra Medical Vision provides AI-powered imaging insights that assist in the early detection of chronic diseases. With a low per-scan cost, it’s accessible to a broader range of medical facilities.
- Use Case: Used widely in radiology to screen for conditions like liver disease, lung conditions, and heart disease.
- Pros: Affordable and accessible, accurate diagnostics.
- Cons: Requires high-quality imaging hardware.
- Price: Zebra Medical Vision offers a subscription starting from around $1 per scan.
- Where to Buy: Zebra Medical Vision tools are available on their website.
Detailed Comparison of AI Solutions in Health Care
Each product serves a unique function in health care:
- IBM Watson Health is ideal for oncologists and medical professionals seeking data-driven treatment support.
- PathAI is well-suited for pathology labs focused on improving diagnostic accuracy for cancer patients.
- Tempus is a premium choice for those seeking highly personalized cancer treatment options.
- Aidoc is invaluable in emergency settings, providing immediate, accurate diagnostics for life-threatening conditions.
- Zebra Medical Vision is accessible to smaller facilities looking for affordable, comprehensive diagnostic tools.
Real-World Use Cases Solved by AI in Health Care
- Early Cancer Detection: Tools like PathAI and Tempus assist in early detection and personalized treatment, which is crucial for improving survival rates in cancer patients.
- Emergency Diagnostics: Aidoc is used in emergency departments to quickly identify critical conditions like brain bleeds, ensuring patients receive immediate care.
- Chronic Disease Screening: Zebra Medical Vision allows clinics to screen patients for chronic diseases affordably, making essential diagnostics accessible.
FAQs
1. How does Artificial Intelligence work in health care?
AI leverages machine learning and data analysis to assist in diagnostics, predict patient outcomes, and personalize treatment plans based on individual health data.
2. What are the main benefits of AI in health care?
AI improves diagnostic accuracy, enables treatment personalization, and increases operational efficiency within health care systems.
3. Where can I buy AI health care solutions?
AI health care products can be acquired directly from the providers’ official websites, where consultations for specific pricing and setup requirements are available.