Top Features of AI and Machine Learning Driving the Future of Technology
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are no longer futuristic concepts; they are integral to how businesses and individuals function today. From powering recommendation engines to enhancing healthcare diagnostics, these technologies have made a profound impact across industries. This article delves deep into what AI and ML are, how they work, their features, and why they are essential. Furthermore, it provides a detailed guide on products leveraging these technologies, complete with real-world applications and buying tips.
Understanding AI and Machine Learning
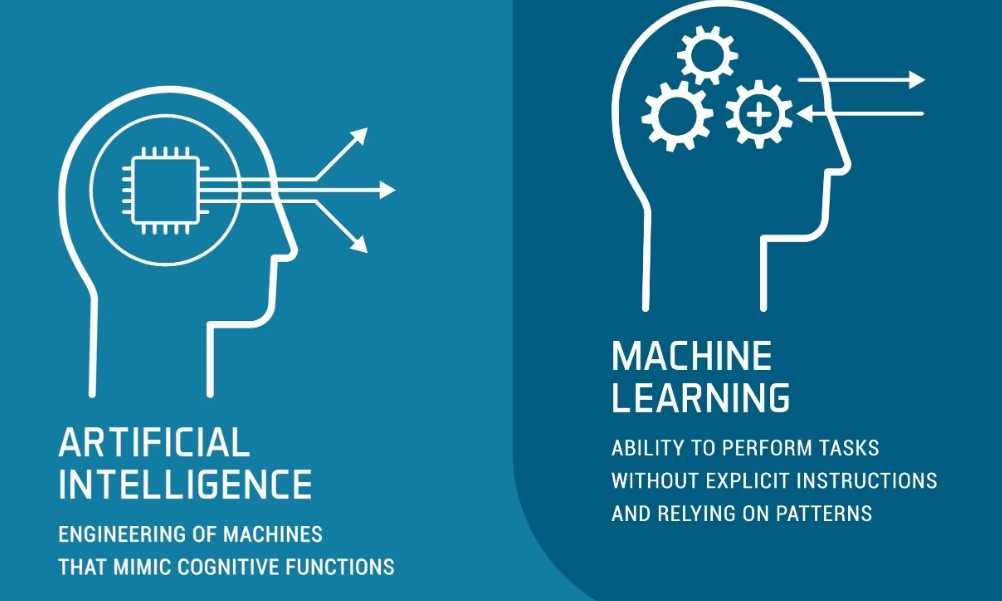
What Is AI?
The simulation of human intellect in robots that are designed to understand, learn, and adapt similarly to humans is known as artificial intelligence. These systems are capable of solving problems, making decisions, and comprehending language—tasks that have historically required human cognition.
For example, AI is the backbone of voice assistants like Siri and Alexa, enabling them to understand commands and provide accurate responses. AI’s capabilities extend to areas like robotics, predictive analytics, and even art creation.
What Is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning, a subset of AI, focuses on algorithms that improve through experience. Instead of being explicitly programmed for every task, ML systems analyze data, identify patterns, and make decisions with minimal human intervention.
For instance, ML powers spam filters in email systems. By learning from labeled examples of spam and non-spam emails, the system improves over time, adapting to new types of spam.
How AI and Machine Learning Work
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are at the heart of modern technology, driving innovations across industries. Understanding how these technologies function requires a closer look at their foundational elements, processes, and real-world applications.
The Basics of AI and ML
AI refers to computer simulation of human intelligence. These systems are programmed to mimic cognitive functions like learning, reasoning, and problem-solving. ML, a subset of AI, focuses on algorithms that improve automatically through experience and data analysis without explicit programming.
The goal of both AI and ML is to enable machines to perform tasks that would typically require human intelligence, such as image recognition, language understanding, and decision-making.
Core Components of AI and ML
- Data Data is the backbone of AI and ML systems. These technologies require vast amounts of structured (e.g., spreadsheets) and unstructured data (e.g., images, text) to learn and improve. The quality and quantity of data significantly impact the system’s performance.For example, an image recognition system is trained using thousands of labeled images, teaching it to distinguish between objects like cars, animals, and buildings.
- Algorithms Algorithms are sets of instructions that enable AI and ML to process data, identify patterns, and make predictions. Depending on the task, algorithms can be:
- Supervised Learning: Trained on labeled data to predict outcomes (e.g., email spam detection).
- Unsupervised Learning: Finds patterns in unlabeled data (e.g., customer segmentation).
- Reinforcement Learning: Learns by interacting with an environment and receiving rewards or penalties (e.g., robotics and game playing).
- Computational Power AI and ML require significant computational resources to process large datasets and execute complex algorithms. High-performance GPUs, cloud computing platforms, and specialized hardware like TPUs (Tensor Processing Units) are commonly used to meet these demands.
How AI Works
- Data Collection AI systems start by collecting and storing data from various sources such as sensors, databases, or user interactions.
- Data Preprocessing The collected data is cleaned and formatted to remove inconsistencies, making it suitable for training AI models.
- Training Models Using algorithms, the system learns from the training data. For instance, an AI system designed for facial recognition analyzes images of faces to identify key features like eyes, noses, and jawlines.
- Inference Once trained, the AI system uses its model to infer or predict outcomes based on new input data. For example, a chatbot understands user queries and generates appropriate responses.
How Machine Learning Works
- Data Input ML systems begin with raw data, which can range from customer purchase histories to sensor readings.
- Feature Extraction Algorithms identify significant features within the data. For example, in a predictive maintenance system, features might include temperature, pressure, and machine usage.
- Model Training The system uses training data to build a model. This involves finding the mathematical relationships between the input data and the desired output.
- Model Validation A separate validation dataset tests the model’s accuracy. Adjustments are made to the model based on its performance.
- Prediction and Refinement The model is deployed to make predictions. Over time, as it encounters more data, the system refines itself to improve accuracy.
Real-World Applications
- Healthcare AI and ML are used for diagnosing diseases from medical images, predicting patient outcomes, and personalizing treatment plans.
- Finance These technologies detect fraudulent transactions, assess credit risks, and optimize investment strategies.
- Retail AI powers personalized product recommendations, dynamic pricing, and supply chain optimization.
Features of AI and Machine Learning

Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) have emerged as transformative technologies, offering advanced capabilities that redefine how industries operate. Their features make them indispensable tools for businesses, researchers, and consumers alike. Below, we explore the key features of AI and ML that highlight their unique functionalities and immense potential.
1. Automation
One of the most significant features of AI and ML is automation. These technologies automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks, reducing the need for human intervention. For example, AI-powered chatbots handle customer queries 24/7, while ML algorithms automate data analysis to uncover insights rapidly. Automation not only increases efficiency but also minimizes errors.
2. Adaptability and Learning
AI and ML systems are inherently adaptable, meaning they can improve over time by learning from new data. Machine Learning, in particular, uses algorithms that allow systems to evolve without explicit reprogramming. For example, recommendation engines like those on Netflix or Amazon adapt to users’ preferences by analyzing past behavior and adjusting recommendations accordingly.
3. Data Processing and Analysis
AI and ML excel at processing and analyzing massive datasets at speeds far beyond human capabilities. This feature is crucial for industries like finance, where algorithms process real-time market data to detect trends, or healthcare, where ML analyzes patient records to predict outcomes. By uncovering patterns in data, these technologies enable better decision-making.
4. Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics is a standout feature of AI and ML. By analyzing historical data, these systems forecast future outcomes, enabling proactive decision-making. For instance, businesses use predictive models to anticipate customer behavior, optimize inventory management, and identify potential risks before they occur.
5. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
AI’s ability to understand and interpret human language is another powerful feature. Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables systems to process text, understand spoken commands, and even translate languages. This capability drives applications like voice assistants (e.g., Siri, Alexa), chatbots, and language translation tools, improving communication between humans and machines.
6. Real-Time Decision Making
AI systems can process data and make decisions in real time. This feature is critical for applications like autonomous vehicles, where AI must analyze road conditions and respond instantly to avoid accidents. In finance, real-time decision-making helps detect fraudulent transactions as they happen.
7. Personalization
AI and ML enable hyper-personalization by tailoring experiences to individual users. E-commerce platforms use these technologies to recommend products based on browsing history, while streaming services suggest content aligned with viewing preferences. Personalization enhances user satisfaction and engagement.
8. Image and Speech Recognition
AI systems equipped with computer vision and speech recognition can interpret visual and auditory inputs. These features are used in applications like facial recognition for security, voice-controlled smart devices, and even in healthcare for analyzing medical imaging.
9. Scalability
AI and ML are designed to scale effortlessly with growing data and operational needs. Whether processing a small dataset or analyzing massive amounts of information, these technologies maintain performance and accuracy, making them suitable for businesses of all sizes.
10. Integration with IoT
AI and ML integrate seamlessly with the Internet of Things (IoT), allowing smart devices to communicate, analyze data, and automate processes. For example, smart home systems use AI to adjust lighting, temperature, and security based on user behavior and preferences.
Benefits of AI and Machine Learning
The adoption of AI and ML offers transformative benefits, ranging from operational efficiency to groundbreaking innovations.
1. Enhanced Operational Efficiency
AI-powered automation replaces repetitive tasks, saving time and reducing errors. For example, chatbots handle routine customer service queries, allowing human agents to focus on complex issues.
2. Cost Reduction
By automating processes, businesses save on labor costs. Additionally, AI’s predictive capabilities optimize supply chains and reduce waste, further lowering expenses.
3. Improved Decision-Making
AI systems analyze data faster and more accurately than humans, supporting better decision-making. In finance, this capability aids in risk management and portfolio optimization.
4. Scalability
AI and ML solutions are highly scalable, adapting to the needs of small startups and large enterprises alike. This scalability ensures that businesses can grow without facing technological bottlenecks.
Real-World Products Using AI and Machine Learning
TensorFlow by Google
TensorFlow is an open-source framework that allows developers to create and train ML models. It is widely used for tasks like image recognition and natural language processing.
Features:
- Cross-platform support for mobile, web, and desktop applications.
- Advanced tools for building deep learning models.
Use Case: TensorFlow is popular among researchers and developers for building AI solutions in fields like healthcare and e-commerce.
Pros:
- Free to use and backed by Google.
- Extensive community and resources for learning.
Cons:
- Requires a steep learning curve for non-programmers.
Amazon SageMaker
Amazon SageMaker is a cloud-based service that simplifies ML development and deployment. It integrates seamlessly with AWS, making it a preferred choice for businesses already using Amazon’s cloud services.
Features:
- Built-in algorithms for various tasks.
- Support for AutoML for non-experts.
Use Case: Retailers use SageMaker for demand forecasting, improving inventory management.
Pros:
- Scalable and flexible pricing models.
- Easy integration with other AWS tools.
Cons:
- May not be cost-effective for small-scale projects.
IBM Watson Studio
IBM Watson Studio provides an integrated environment for building and training AI models. It is widely used for text analytics and predictive modeling.
Features:
- Drag-and-drop interface for ease of use.
- Access to IBM’s extensive AI libraries.
Use Case: Financial institutions use Watson for sentiment analysis and credit risk assessment.
Pros:
- User-friendly for beginners.
- Robust security features.
Cons:
- Higher cost compared to other tools.
Use Cases of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) have become integral to modern technology, driving innovation and efficiency across various industries. Below are some of the most impactful use cases, demonstrating their versatility and value.
1. Healthcare
AI and ML have revolutionized healthcare by enhancing diagnostics, treatment planning, and patient care.
- Medical Imaging: AI-powered systems analyze X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans to detect diseases like cancer and heart conditions with remarkable accuracy.
- Predictive Analytics: ML models predict patient outcomes by analyzing historical data, aiding in proactive healthcare measures.
- Personalized Treatment: AI tailors treatment plans based on individual patient data, improving outcomes while reducing side effects.
For example, IBM Watson Health uses AI to assist doctors in diagnosing diseases and recommending treatment options.
2. Finance
In finance, AI and ML improve risk management, fraud detection, and customer service.
- Fraud Detection: ML algorithms analyze transaction patterns to identify and flag fraudulent activities in real time.
- Credit Scoring: AI evaluates creditworthiness by analyzing financial histories, enabling fairer lending decisions.
- Algorithmic Trading: AI-powered trading systems predict market trends and execute trades, maximizing profits.
Major financial institutions like JPMorgan Chase use AI tools for trading and fraud detection.
3. Retail and E-commerce
AI and ML drive personalization and operational efficiency in retail and e-commerce.
- Product Recommendations: ML algorithms analyze customer behavior to suggest products, increasing sales and customer satisfaction.
- Dynamic Pricing: AI adjusts prices in real time based on demand, competition, and inventory levels.
- Inventory Management: Predictive analytics optimize stock levels, minimizing overstocking and shortages.
Amazon employs AI to enhance customer experience and streamline logistics.
4. Manufacturing
AI and ML improve efficiency and safety in manufacturing processes.
- Predictive Maintenance: ML predicts equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and repair costs.
- Quality Control: AI systems analyze production lines to detect defects, ensuring product quality.
- Robotics: AI-powered robots perform repetitive or hazardous tasks, enhancing workplace safety.
For instance, General Electric uses AI for predictive maintenance across its industrial equipment.
5. Transportation
AI and ML are transforming transportation through automation and optimization.
- Autonomous Vehicles: AI enables self-driving cars to navigate roads and make real-time decisions, improving safety and efficiency.
- Route Optimization: ML analyzes traffic data to suggest the fastest and most fuel-efficient routes.
- Logistics Management: AI optimizes supply chains by predicting demand and streamlining deliveries.
Tesla’s AI-powered Autopilot is a leading example of autonomous vehicle technology.
FAQs
What are the key differences between AI and Machine Learning?
AI is a broader concept of machines mimicking human intelligence, while Machine Learning is a subset of AI focusing on systems learning from data to improve over time.
Can small businesses afford AI and Machine Learning tools?
Yes, many tools like TensorFlow and H2O.ai are free or offer affordable plans, making AI accessible to small businesses.
What industries benefit most from AI and Machine Learning?
Industries like healthcare, retail, finance, and manufacturing see the most significant benefits, including improved efficiency and enhanced customer experiences.






